Paralysis is a complex medical condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It occurs when there is a loss of muscle function in a part of the body, often due to damage to the nervous system. This impairment can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, affecting their ability to move and perform daily tasks. Understanding the different types of paralysis is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and management of the condition. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various types of paralysis, their causes, and implications.
What is Paralysis?
Paralysis is defined as the loss of muscle function in a part of the body. It can be partial, affecting only specific muscles or muscle groups, or complete, resulting in the inability to move the affected area altogether. Paralysis can occur due to various reasons, including traumatic injuries, neurological disorders, infections, or diseases.
Types of Paralysis
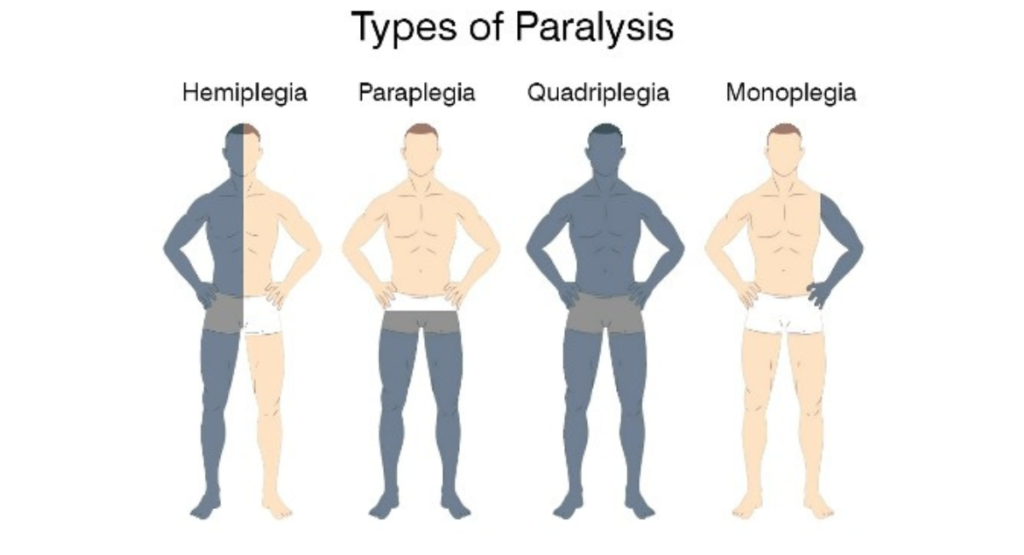
Monoplegia
Monoplegia is a type of paralysis that affects only one limb, such as an arm or a leg. It is often caused by damage to the nerves or spinal cord in the affected limb. Monoplegia can result from conditions such as stroke, traumatic injury, or nerve damage.
Hemiplegia
Hemiplegia refers to paralysis that affects one side of the body, including the arm, leg, and sometimes the face. It is commonly associated with stroke, where damage to the brain’s motor cortex disrupts signals to one side of the body. Other causes of hemiplegia include brain injuries, tumors, and certain neurological conditions.
Paraplegia
Paraplegia involves paralysis of the lower half of the body, including both legs and possibly the lower trunk. It typically occurs due to spinal cord injuries below the neck, affecting the communication between the brain and the lower body. Spinal cord trauma, such as from accidents or falls, is the primary cause of paraplegia.
Quadriplegia (Tetraplegia)
Quadriplegia, also known as tetraplegia, is the most severe form of paralysis, affecting all four limbs and often the torso. It results from significant damage to the spinal cord in the cervical (neck) region. Individuals with quadriplegia may experience varying degrees of impairment in motor and sensory functions, depending on the extent of the injury.
Paresis
Paresis refers to partial paralysis or weakness in a part of the body, resulting in reduced muscle strength and control. Unlike complete paralysis, paresis allows some movement in the affected area, although it may be limited or impaired. Paresis can occur due to nerve damage, muscle disorders, or neurological conditions.
Causes of Paralysis
Paralysis can be caused by a wide range of factors, including:
Traumatic Injuries: Severe blows or trauma to the head, neck, or spine can damage the nerves and lead to paralysis.
Neurological Disorders: Conditions such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and Guillain-Barré syndrome can disrupt nerve function and cause paralysis.
Spinal Cord Injuries: Damage to the spinal cord, resulting from accidents, falls, or medical procedures, can cause various types of paralysis.
Infections: Certain infections, such as polio, meningitis, and encephalitis, can damage the nerves and lead to paralysis.
Genetic Disorders: Inherited conditions like cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy can cause paralysis or muscle weakness from birth or early childhood.
Implications of Paralysis
Paralysis can have profound physical, emotional, and social implications for affected individuals and their families. Some of the common consequences of paralysis include:
Loss of Mobility: Paralysis restricts movement and can lead to dependence on assistive devices or caregivers for daily activities.
Chronic Pain: Nerve damage associated with paralysis can cause chronic pain and discomfort in the affected area.
Secondary Health Issues: Immobility and loss of sensation increase the risk of secondary health problems such as pressure sores, urinary tract infections, and respiratory complications.
Emotional Distress: Coping with the physical limitations and lifestyle changes resulting from paralysis can lead to feelings of depression, anxiety, and social isolation.
Financial Burden: The cost of medical care, assistive devices, and ongoing therapy can impose a significant financial burden on individuals and their families.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of paralysis and their underlying causes is essential for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and support for affected individuals. While paralysis presents significant challenges, advancements in medical technology and rehabilitation techniques offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life. By raising awareness and promoting research into paralysis prevention and treatment, we can strive towards a future where individuals with paralysis can lead fulfilling and independent lives.
We are India’s first comprehensive continuum care provider. We provide multidisciplinary out of hospital care to acute and post-acute and chronically ill patients at our critical care facilities and your home.