When individuals face serious illnesses and require specialized care, the terms “palliative care vs hospice care” often come up. While both approaches focus on providing support and improving quality of life, there are distinct differences between palliative care and hospice care. This blog will explore the nuances, benefits, and limitations of each, palliative care and hospice care comparison to help individuals and their families make informed decisions regarding their care. We will delve into the differences between palliative care vs hospice care, the comparison between end-of-life care and comfort care, and discuss the benefits and limitations of hospice care.
What is Palliative Care?
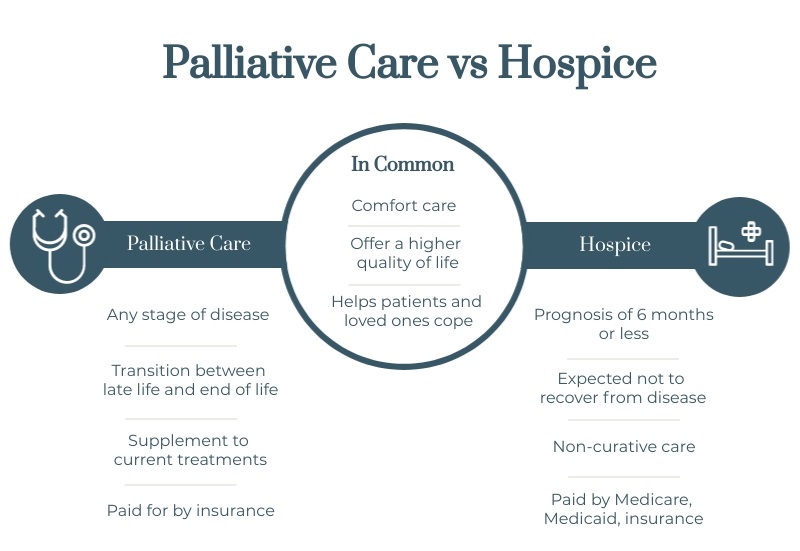
Palliative care is a holistic approach that aims to improve the quality of life for individuals facing serious illnesses, regardless of their prognosis. It focuses on relieving pain, managing symptoms, and addressing the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of patients. Palliative care can be provided alongside curative treatments and is not limited to end-of-life care.
What is Hospice Care?
Hospice care, on the other hand, is a specialized form of care that is primarily focused on providing comfort and support for individuals who have a prognosis of six months or less to live. It is typically initiated when curative treatments are no longer effective or desired, and the primary goal becomes maximizing the quality of life during the end stages of life.
Palliative Care vs Hospice Care
Several factors differ Palliative care from Hospice care, including:
- Timing and Prognosis: The key difference between palliative care vs hospice care lies in the timing and prognosis. Palliative care can be initiated at any stage of a serious illness, whereas hospice care is specifically for individuals nearing the end of life with a limited life expectancy.
- Treatment Goals: Palliative care aims to provide relief from symptoms, improve quality of life, and support patients in pursuing curative or life-prolonging treatments. Hospice care, however, focuses on providing comfort and support, with the primary goal being to enhance the quality of life during the final stages of life.
- Scope of Care: Palliative care encompasses a broader range of services, including pain and symptom management, emotional and psychological support, spiritual care, and assistance with decision-making. Hospice care, while also addressing these aspects, has a more concentrated focus on end-of-life care and providing comfort to patients and their families.
- Location of Care: Palliative care can be provided in various settings, such as hospitals, clinics, or the patient’s home. Hospice care is often delivered in the patient’s home or in specialized hospice facilities, providing a comfortable and supportive environment for end-of-life care.
- Eligibility Criteria: To receive palliative care, individuals can be at any stage of their illness and continue to pursue curative treatments. In contrast, hospice care requires individuals to have a prognosis of six months or less to live and forgo further curative treatments.

Benefits and Limitations of Hospice Care:
Hospice care offers several benefits, including:
- Expert pain and symptom management: Hospice care focuses on providing effective pain management and alleviating distressing symptoms to maximize comfort.
- Emotional and spiritual support: Hospice care teams provide emotional and spiritual support to patients and their families, helping them navigate the challenges of the end-of-life journey.
- Caregiver support: Hospice care recognizes the significant role of caregivers and offers support services to help alleviate their burden and provide respite.
However, there are limitations to hospice care as well, such as:
- Limited life expectancy requirement: Hospice care is only available for individuals with a prognosis of six months or less to live, which can exclude some individuals who may benefit from comfort-focused care but do not meet the specific timeframe criteria.
- No curative treatments: Hospice care focuses solely on comfort care, which means that individuals who wish to continue pursuing curative or life-prolonging treatments may not be eligible for hospice care.
- Limited access to certain medical interventions: Hospice care generally prioritizes comfort and quality of life over aggressive medical interventions. This means that certain treatments or interventions that aim to prolong life or address specific conditions may not be pursued under hospice care.
Benefits and Limitations of Palliative Care:
Palliative care offers numerous benefits for individuals facing serious illnesses, including:
Holistic Care: Palliative care takes a comprehensive approach, addressing the physical, emotional, psychological, and spiritual needs of patients.
Symptom Management: Palliative care specialists are trained in effective pain management and symptom control. They work closely with patients to alleviate pain, manage symptoms such as nausea, fatigue, and shortness of breath, and enhance overall comfort.
Enhanced Quality of Life: By focusing on the relief of symptoms and improving overall well-being, palliative care aims to enhance the quality of life for patients.
Despite its many benefits, there are certain limitations to consider with palliative care:
Limited Availability: Access to specialized palliative care services may vary based on geographical location, healthcare resources, and healthcare systems.
Resource Constraints: Palliative care may face limitations due to resource constraints, such as the availability of trained specialists, access to medications, or financial constraints that impact the scope and intensity of services provided.
Complex Medical Conditions: Palliative care may face challenges in managing complex medical conditions with multiple comorbidities.
Palliative care vs hospice care: Which is Better?
The choice between palliative care and hospice care depends on an individual’s specific needs, goals, and stage of illness. Palliative care can be beneficial at any stage of a serious illness, providing relief from symptoms, support for decision-making, and holistic care. Hospice care, on the other hand, is specifically designed for end-of-life care, prioritizing comfort and support during the final stages of life.
It is important to note that palliative care and hospice care are not mutually exclusive. In some cases, individuals may transition from palliative care to hospice care as their condition progresses and their focus shifts toward end-of-life care. The choice between the two depends on the individual’s goals, prognosis, and preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions
- When is palliative care appropriate compared to hospice care?
Palliative care is appropriate at any stage of a serious illness, whereas hospice care is specifically for individuals with a life expectancy of six months or less.
- Do palliative care and hospice care focus on the same goals?
Yes, both palliative care and hospice care focus on improving the quality of life for patients. They aim to provide comfort, alleviate symptoms, and address the physical, emotional, and spiritual needs of individuals facing serious illnesses.
- Is hospice care only for those at the end of life, or can it be used earlier?
Hospice care is primarily intended for individuals with a life expectancy of six months or less. However, it can be initiated earlier if the patient’s condition indicates a need for end-of-life care and symptom management.
- What are the main components of palliative care and hospice care?
The main components of palliative care vs hospice care include pain and symptom management, emotional support, spiritual care, and enhanced quality of life for patients and their families.
We are India’s first comprehensive continuum care provider. We provide multidisciplinary out of hospital care to acute and post-acute and chronically ill patients at our critical care facilities and your home.