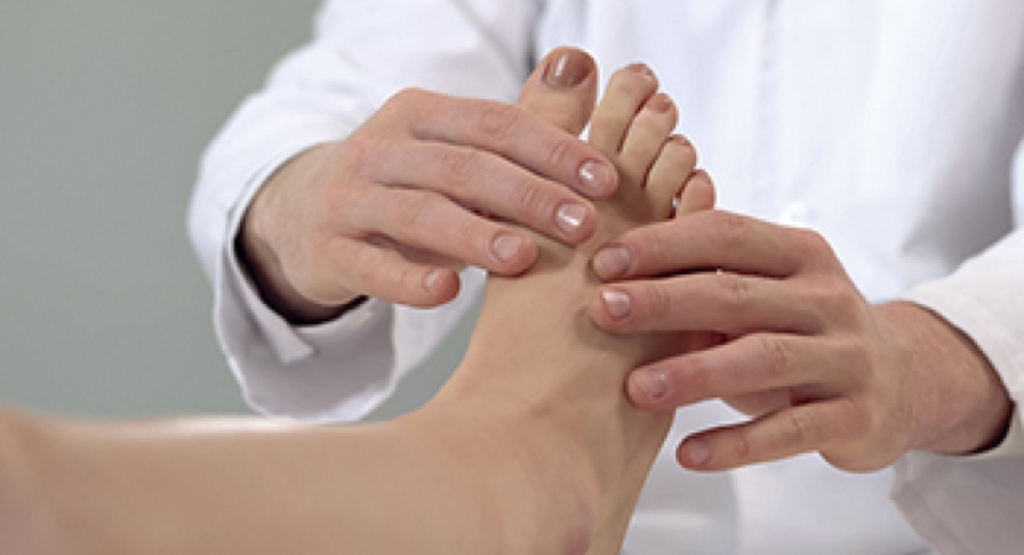
Ankle pain, though commonly associated with injuries and sprains, can sometimes manifest without any apparent trauma. When ankle pain arises without a clear injury, individuals may find themselves grappling with discomfort and uncertainty about its origin. In this exploration, we’ll delve into the various causes of ankle pain without injury, shedding light on potential underlying issues and effective treatment approaches.
Common Causes of Ankle Pain Without Injury
Ankle pain without injury can be attributed to various underlying causes, often involving conditions related to overuse, inflammation, or structural issues. Here are some common causes of ankle pain without injury:
- Overuse and Strain: Prolonged periods of standing, walking, or engaging in repetitive motions can strain the muscles and ligaments around the ankle, leading to pain. Overuse injuries may result from activities such as long-distance running, excessive walking, or standing for extended periods.
- Arthritis: Both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can affect the joints, including those in the ankle. Inflammation in the joints can cause pain and stiffness, even in the absence of a specific injury.
- Tendinitis: Tendinitis involves inflammation of the tendons, often due to repetitive movements or overuse. The Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone, is particularly susceptible to tendinitis and can cause pain in the back of the ankle.
- Nerve Compression or Impingement: Conditions such as tarsal tunnel syndrome or nerve impingement can result in ankle pain without injury. Compression of nerves in the ankle can lead to tingling, numbness, and pain.
- Flat Feet or Fallen Arches: Structural issues like flat feet or fallen arches can contribute to ankle pain. The lack of proper arch support may strain the ligaments and tendons, causing discomfort.
- Gout: Gout is a form of arthritis characterized by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, often affecting the big toe. However, it can also cause pain in other joints, including the ankle.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Conditions like lupus or psoriatic arthritis, which involve inflammation throughout the body, can affect the ankles and lead to pain.
- Infections: Infections, though less common, can cause ankle pain without injury. Cellulitis, a bacterial skin infection, can spread to the ankle and result in localized pain and swelling.
Effective Treatment Approaches
The treatment of ankle pain without injury depends on the underlying cause. Here are some effective treatment approaches that healthcare professionals may recommend:
- Rest and Elevation: Regardless of the cause, providing the affected ankle with adequate rest is crucial for the healing process. Elevating the leg when at rest helps reduce swelling.
- Ice and Compression: Applying ice packs and using compression bandages can help alleviate pain and inflammation. Be cautious not to apply ice directly to the skin and use a cloth or towel as a barrier.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, can provide relief by reducing pain and inflammation. However, these should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design exercises to strengthen the muscles around the ankle and improve flexibility. Physical therapy is particularly beneficial for issues related to overuse or muscle imbalances.
- Orthotics: For individuals with flat feet or fallen arches, orthotic inserts can provide support and help distribute weight more evenly, reducing strain on the ankle.
- Bracing or Splinting: In some cases, using ankle braces or splints can provide additional support, especially during activities that may exacerbate pain.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making adjustments to daily activities, such as wearing supportive footwear, avoiding prolonged standing, and incorporating rest breaks, can contribute to pain management.
- Medication for Underlying Conditions: If the ankle pain is related to an underlying condition such as arthritis or gout, medications targeted at managing these conditions may be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases of severe inflammation, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to provide targeted relief. However, these injections come with potential side effects and should be administered under medical supervision.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seeking medical attention for ankle pain without injury is crucial to accurately diagnose the underlying cause and implement appropriate treatment. While some mild discomfort may resolve with rest and home care, certain signs and symptoms warrant prompt medical evaluation. Here are situations in which individuals should seek medical attention for ankle pain without injury:
- Persistent Pain: If ankle pain persists or worsens over time, it indicates that the underlying issue may require professional evaluation. Chronic pain without improvement may be a sign of an unresolved problem.
- Significant Swelling: Excessive swelling around the ankle joint, especially if it is accompanied by warmth and redness, can be indicative of inflammation or an underlying condition. This requires investigation to determine the cause.
- Inability to Bear Weight: If the pain is severe enough to prevent bearing weight on the affected ankle, it suggests a more significant issue such as a fracture, severe sprain, or another structural problem that requires medical attention.
- Changes in Skin Color: Discoloration of the skin around the ankle, such as bruising or unusual pigmentation, may indicate internal bleeding, severe inflammation, or vascular issues. These symptoms should not be ignored.
- Fever or Chills: The presence of systemic symptoms like fever and chills may suggest an underlying infection, especially if the ankle pain is accompanied by redness and increased warmth in the affected area.
- History of Trauma: If there is a history of trauma or injury to the ankle, even if it seems minor, it is advisable to seek medical attention. Fractures, ligament injuries, and other structural issues may not always be immediately apparent.
Conclusion
Ankle pain without injury can be a perplexing and uncomfortable experience, but understanding its potential causes is the first step toward effective management. From overuse and arthritis to structural issues and inflammatory conditions, a range of factors can contribute to ankle discomfort. By adopting a comprehensive approach that includes rest, targeted exercises, and medical intervention when necessary, individuals can navigate the journey to recovery with informed decisions and proactive care. If in doubt, consulting with a healthcare professional ensures a tailored treatment plan, addressing the specific underlying cause of the ankle pain without injury and promoting long-term joint health.
We are India’s first comprehensive continuum care provider. We provide multidisciplinary out of hospital care to acute and post-acute and chronically ill patients at our critical care facilities and your home.


