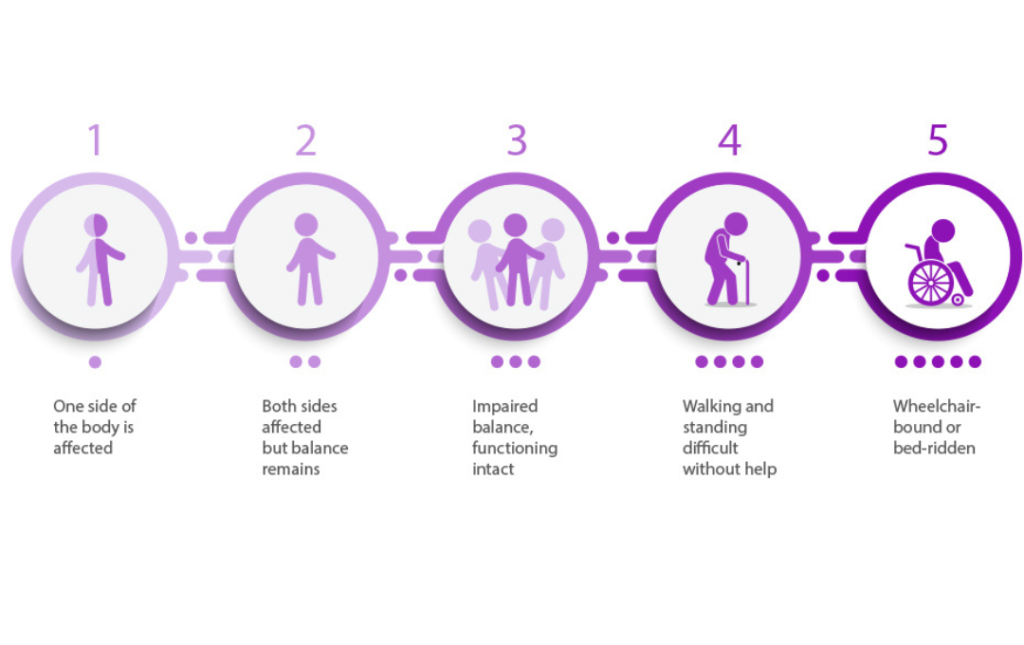
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a complex neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. As we delve into the topic of understanding Parkinson’s Disease development stages, it’s important to recognize that the disease progression can be categorized into distinct phases, commonly referred to as the 5 stages of Parkinson’s Disease. This blog aims to provide an in-depth exploration of these stages, shedding light on the Parkinson’s Disease timeline and stages, symptom progression, patient journey, treatment options at different stages, and strategies for managing Parkinson’s Disease stages.
5 Stages of Parkinson’s Disease
Stage 1: Early Parkinson’s Disease
The journey through Parkinson’s Disease progression stages begins with the subtle and often elusive signs of the early stage. This initial phase, known as Stage 1, is characterized by the emergence of mild motor symptoms that may go unnoticed or be attributed to other factors. Understanding this crucial stage is essential for early detection, intervention, and improved long-term outcomes.
Symptoms and Characteristics:
In Stage 1 of Parkinson’s Disease, individuals may experience one or more of the following symptoms:
1. Tremors: The hallmark tremor associated with Parkinson’s Disease often starts in one hand and is most noticeable when the hand is at rest. Tremors can also affect the legs, chin, or other parts of the body.
2. Changes in Posture and Balance: Subtle changes in posture, such as stooping or leaning, might occur. Balance may become slightly affected, leading to a feeling of unsteadiness.
3. Micrographia: Handwriting may become smaller and more cramped, reflecting changes in fine motor control.
4. Loss of Smell: An impaired sense of smell, known as anosmia, can be an early indicator of Parkinson’s Disease.
Lifestyle Modifications and Treatment:
The following strategies can help individuals manage early-stage Parkinson’s Disease:
1. Physical Therapy: Working with a physical therapist can help maintain mobility, improve balance, and prevent muscle stiffness.
2. Occupational Therapy: Occupational therapists can provide strategies to manage daily tasks more efficiently and enhance independence.
3. Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in nutrients and antioxidants supports overall health and may have a positive impact on brain function.
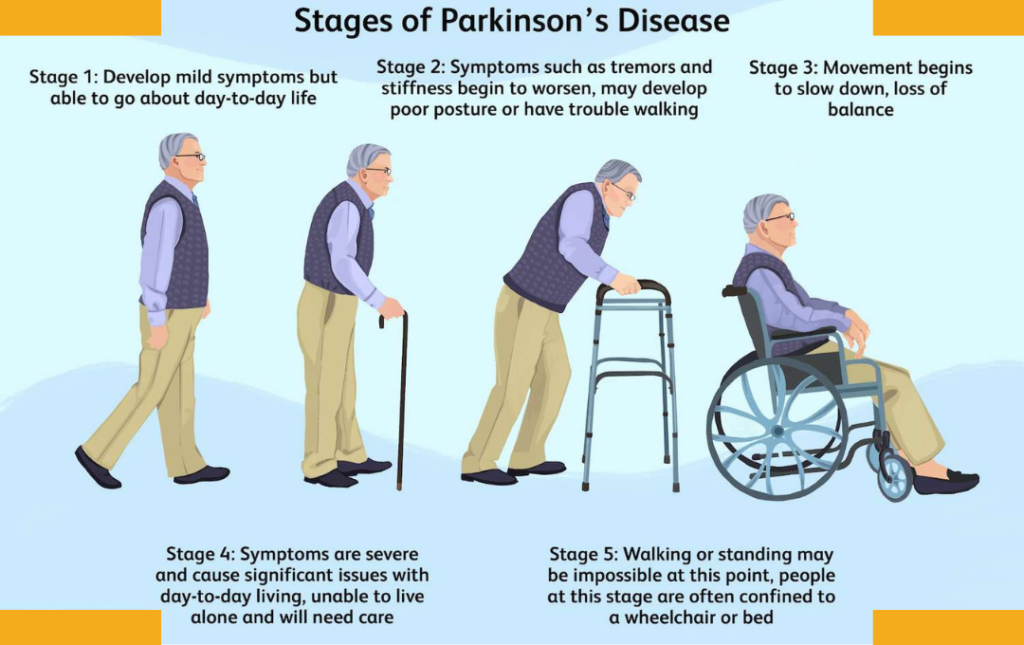
Stage 2: Mild Parkinson’s Disease
As the journey through Parkinson’s Disease continues, individuals enter Stage 2, which is characterized by the progression of symptoms and a noticeable impact on daily life. While still considered early in the disease’s course, Parkinson’s Disease severity levels mark a significant shift as motor symptoms become more pronounced and may begin to affect both sides of the body.
Symptoms and Characteristics:
During Stage 2 of Parkinson’s Disease, the following symptoms may become more evident and impactful:
1. Bilateral Symptoms: Motor symptoms that were previously limited to one side of the body, such as tremors or bradykinesia, may now affect both sides.
2. Balance Challenges: Balance problems may increase, leading to a higher risk of falls. Instability and unsteadiness can impact daily activities and mobility.
3. Fine Motor Control: Tasks requiring precise hand movements, such as buttoning clothes or using utensils, may become more challenging due to decreased fine motor control.
4. Motor Fluctuations: Individuals may experience “on-off” periods, where medications’ effectiveness fluctuates, leading to unpredictable variations in Parkinson’s Disease symptom progression severity.
Lifestyle Modifications and Treatment:
In Stage 2, a combination of medication and lifestyle modifications continues to be crucial in managing symptoms and enhancing well-being:
1. Medication Adjustments: Neurologists may fine-tune medication dosages or introduce new medications to manage motor fluctuations and control symptoms.
2. Speech Therapy: Individuals experiencing changes in voice modulation or speech clarity can benefit from speech therapy sessions that aim to improve communication skills.
3. Nutrition and Hydration: A balanced diet and proper hydration are essential for overall health and may impact medication absorption and effectiveness.
Stage 3: Moderate Parkinson’s Disease
As individuals progress along their Parkinson’s Disease journey, they may enter Stage 3, a phase marked by more significant motor symptoms and increasing challenges with daily activities. This stage, often referred to as the moderate stage, requires a comprehensive approach to management and a focus on maintaining independence and quality of life.
Symptoms and Characteristics:
Some key features of this stage include:
1. Motor Symptoms: Rigidity and bradykinesia continue to progress, affecting muscle flexibility and movement speed. Tremors may remain present and can affect various parts of the body.
2. Speech Changes: Speech may become softer, less clear, and more monotone. Communication challenges can contribute to difficulties in social interactions.
3. Emotional and Cognitive Changes: Non-motor symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and cognitive changes may become more noticeable. Memory, attention, and decision-making abilities could be affected.
4. Activities of Daily Living: Routine tasks such as dressing, bathing, and eating may require increased effort or assistance. Fine motor skills continue to decline, impacting tasks that involve intricate hand movements.
Lifestyle Modifications and Treatment:
Managing Parkinson’s Disease stages involves a comprehensive approach to address both motor and non-motor symptoms:
1. Cognitive Stimulation: Engaging in cognitive exercises, puzzles, and games can help maintain cognitive function and mental agility.
2. Assistive Devices: Depending on individual needs, assistive devices such as walkers, canes, or adaptive utensils may be introduced to enhance independence.
3. Nutrition and Hydration: Proper nutrition and hydration are essential to support overall health and well-being.
Stage 4: Advanced Parkinson’s Disease
As the Parkinson’s Disease patient journey continues, individuals may find themselves entering Stage 4, a phase characterized by significant motor symptoms and increasing challenges to daily functioning. In this advanced stage, individuals and their caregivers face unique obstacles, but with the right strategies and support, it’s possible to maintain a fulfilling life.
Symptoms and Characteristics:
Stage 4 of Parkinson’s Disease is marked by a further escalation of motor and non-motor symptoms, which may include:
1. Severe Motor Symptoms: Rigidity and bradykinesia continue to progress, and movement becomes increasingly challenging. Tremors may persist and impact various parts of the body.
2. Limited Mobility: Individuals may experience difficulty walking and require assistance or mobility aids such as a walker or wheelchair. Falls become more frequent due to instability.
3. Communication Difficulties: Speech may become very soft or unintelligible. Difficulty in swallowing may lead to drooling or choking during meals.
4. Motor Fluctuations: Severe motor fluctuations, known as “on-off” fluctuations, become more pronounced, and medication effectiveness becomes less predictable.
Lifestyle Modifications and Treatment:
Parkinson’s Disease early and advanced stages management involves a comprehensive approach to address the complex challenges that arise:
1. Physical and Occupational Therapy: Ongoing therapy sessions focus on maintaining functional mobility, preventing contractures, and optimizing the use of assistive devices.
2. Nutrition and Hydration: Ensuring proper nutrition and hydration is vital for overall health, especially considering the potential challenges of swallowing.
3. Emotional Support: Caregivers and individuals alike may benefit from support groups, counseling, and mindfulness techniques to manage emotional challenges.
Stage 5: Severe Parkinson’s Disease
The journey through Parkinson’s Disease may lead individuals and their caregivers to Stage 5, the most advanced and challenging phase of the disease. In this stage, the profound impact of motor and non-motor symptoms requires comprehensive care, unwavering support, and a focus on maintaining dignity and comfort.
Symptoms and Characteristics:
Stage 5 of Parkinson’s Disease is characterized by severe motor and non-motor symptoms that significantly affect daily life:
1. Communication Difficulties: Speech may be nearly unintelligible, and individuals might rely on communication boards or assistive devices to express their needs.
2. Swallowing Challenges: Swallowing difficulties can lead to an increased risk of aspiration, impacting nutrition and hydration.
3. Dependence on Caregivers: Individuals require constant care and assistance with all aspects of daily life, including personal hygiene, mobility, and medication management.
4. Limited Independence: Independence becomes extremely limited, and individuals are often bedridden or wheelchair-bound.
Lifestyle Modifications and Treatment:
Managing Stage 5 of Parkinson’s Disease centers on optimizing comfort, dignity, and overall well-being:
1. Nutrition and Hydration: Specialized diets, feeding tubes, or nutritional supplements may be necessary to ensure proper nourishment.
2. Skin Care and Mobility: Regular repositioning and skin care are vital to prevent pressure sores, and assistive devices can provide comfort and support.
3. Emotional Support: Providing emotional comfort and companionship to individuals and their caregivers is crucial in this stage.
Conclusion
Exploring the 5 stages of Parkinson’s Disease offers valuable insights into the evolving nature of this neurodegenerative disorder. From the early and mild stages characterized by subtle symptoms to the advanced stages that significantly impact daily life, understanding Parkinson’s Disease progression stages is crucial for effective management and care. As medical research and treatment options continue to advance, individuals and their families can look forward to a future with improved outcomes and a better quality of life at every stage of Parkinson’s Disease.
We are India’s first comprehensive continuum care provider. We provide multidisciplinary out of hospital care to acute and post-acute and chronically ill patients at our critical care facilities and your home.